n 1912, the
Picture House, in
Clevedon,
England, opened with a charity film performance to raise funds for the victims of the
Titanic disaster, and has been showing films continuously since. The 1913 opening of the
Regent Theater in
New York City signaled a new respectability for the medium, and the start of the two-decade heyday of American cinema design. The million dollar
Mark Strand Theater at 47th Street and Broadway in
New York City opened in 1914 by
Mitchell Mark was the archetypical movie palace. The ornate
Al Ringling Theater was the very first "Movie Palace" it was built in Baraboo, WI by Al Ringling, one of the founders of the Ringling Bros.
Circus for the then incredible sum of $100,000.00. In 1915, the movie
The Birth of a Nation would also pave way for
feature films.
[6] By 1915, feature films were so successful that the five cent ticket admission prices would expand to ten cents, hence ending the era of nickelodeon movie theaters.
[7] Later, Los Angeles promoter
Sid Grauman continued the trend of theatre-as-destination with his ornate "
Million Dollar Theatre", using the same design firm as Ringling (the MDT was the first to signify its primary use for motion pictures with the "theatre" spelling), and opened on Broadway in
downtown Los Angeles in 1918.
Post 1920s : modern era
In the next ten years, as movie revenues exploded, independent promoters and movie studios (who owned their own proprietary chains until an
antitrust ruling in 1948) raced to build the most lavish, elaborate, attractive theatres. These forms morphed into a unique architectural genre—the
movie palace—a unique and extreme architectural genre which boasted a luxurious design, a giant screen, and, beginning in 1953,
stereophonic sound. The movie chains were also among the first industries to install
air conditioning systems which gave the theatres an additional lure of comfort in the summer period. In addition in the early 1931 a chair was designed, where the person sitting could move back so other patrons could easily leave their seats during the
movie showing. This type of seat became standard in almost all US movie theaters.
[8]In the 1970s,
porn theatres became ubiquitous in some areas. However, the introduction of the low-cost
VHS video system for home televisions has decommissioned many porno
cinemas as well as many 'second-run' theatres.
People can pay to watch movies at home after a few short months following their theatrical release, through
cable television or
streamed from the Internet:
pay-per-view (PPV) and
video on demand (VOD). Initially, home video contributed to an industry wide slump in the late 1980s (see
disruptive technology), not to mention the decline of the 'Dollar Cinema' (where first-run films are pulled from circulation to play at reduced rates for the remainder of their run). The theater industry responded by building larger auditoriums with
stadium seating layouts, installing more screens (to allow for more variety and more show times), upgrading sound systems and installing more amenities and higher-quality food and drink. The growing popularity of
high-definition television sets, along with
HD DVD and
Blu-ray Disc players may also contribute to the decline in cinema attendance, although there seems to be little evidence of this at the moment. As of June 12, 2009 all US television stations started broadcasting in the
digital format. This could also affect US movie theaters.
[citation needed]3D
3-D film is a system of presenting film images so that they appear to the viewer to be three-dimensional. Visitors usually borrow or keep special glasses to wear while watching the film. Depending on the system used, these are typically
polarized glasses. Three-dimensional films use two images channelled, respectively, to the right and left eyes to simulate depth by using 3-D glasses with red and blue lenses (anaglyph), polarized (linear and circular), and other techniques. 3-D glasses deliver the proper image to the proper eye and make the image appear to "pop-out" at the viewer and even follow the viewer when he/she moves so viewers relatively see the same image. Most 3-D films are shown in
amusement parks and even "4-D" techniques are used when certain effects such as spraying of water, movement of seats, and other effects are used to simulate actions seen on the screen. The earliest 3-D films were presented in the 1920s. There have been several "waves" of 3D film distribution, most notably in the 1950s when they were promoted as a way to offer audiences something that they could not see at home on television. Still the process faded quickly and as yet has never been more than a periodic novelty in film presentation. Currently, films are again being presented in cinemas in 3-D, in the
IMAX 3D system and in digital 3-D, such as is used in the animated films of
Disney/
Pixar.
In 2009, Ben Walters suggested that film exhibitors are now more interested in 3-D film. The number of 3-D screens in theaters is increasing (
Real D company expects 15,000 screens worldwide in 2010). 3-D films encourage exhibitors to adopt
digital cinema and provide a way to compete with home theaters. One incentive for 3-D screens is that although ticket sales decline, revenues from 3-D tickets grow.
[9]The RealD 3D system works by using a single digital projector, that swaps back and forth between the images for each eye. A filter is placed in front of the projector that changes the polarisation of the light coming from the projector. A silver screen is used to reflect this light back at the audience and reduce loss of brightness. RealD is the most popular system, but there are three other systems available: Master Image, XpanD and
Dolby 3D.
When a system is used that requires inexpensive 3D glasses, they can sometimes be kept by the visitor. In most theaters the price is not simply for the glasses, but for the experience of 3D. Most theatres have a fixed cost for 3D, while others charge for the glasses, but the latter is uncommon (at least in the United States). For example, in
Pathé theaters in the Netherlands the extra fee for watching a 3D film consists of a fixed fee of € 1.50, and an optional fee of €1 for the glasses.
[10]IMAX
IMAX is a system using film with more than ten times the frame size of a
35 mm film to produce image quality far superior to conventional film. IMAX theaters use an oversized screen as well as special projectors. Invented by a Canadian company, the first permanent IMAX theater was at
Ontario Place in
Toronto,
Ontario,
Canada.
Design

Interior of a 1950s style
fine arts movietheater. A low pitch viewing floor is used.
In conventional low pitch viewing floors the preferred
seating arrangement is to use staggered rows. While a less efficient use of floor space this allows a somewhat improved sight line between the patrons seated in the next row toward the screen, provided they do not lean toward one another.
"
Stadium seating", popular in modern multiplexes, actually dates back to the 1920s. The 1922 Princess Theatre in Honolulu, Hawaii featured "stadium seating," sharply raked rows of seats extending from in front of the screen back towards the ceiling. It gives patrons a clear sight line over the heads of those seated in front of them. Modern "stadium seating" was utilized in
IMAX theatres, which have very tall screens, beginning in the early 1970s.
Rows of seats are divided by one or more aisles so that there are seldom more than 20 seats in a row. This allows easier access to seating, as the space between rows is very narrow. Depending on the angle of rake of the seats, the aisles have steps. In older theaters, aisle lights were often built into the end seats of each row to help patrons find their way in the dark. Since the advent of stadium theaters with stepped aisles, each step in the aisles may be outlined with small
lights to prevent patrons from tripping in the darkened theater.
Theaters often have booster seats for children and other short people to put on the seat, to sit higher, for a better view.
Multiplexes and megaplexes
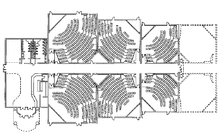
Example of a Multiplex layout
Canada was the first country in the world to have a two-screen theater. The
Elgin Theatre in
Ottawa became the first venue to offer two film programs on different screens in 1957 when Canadian theater-owner
Nat Taylor converted the dual screen theater into one capable of showing two different films simultaneously.
In the United States, Stanley Durwood of American Multi-Cinema (now
AMC Theatres) is credited as pioneering the
multiplex in 1963 after realizing that he could operate several attached auditoriums with the same staff needed for one through careful management of the start times for each movie. Ward Parkway Center in Kansas City, Missouri had the first multiplex cinema in the United States.
Since the 1960s, multiple-screen theatres have become the norm, and many existing venues have been retrofitted so that they have multiple auditoriums. A single foyer area is shared among them. In the 1970s many large 1920s
movie palaces were converted into multiple screen venues by dividing their large auditoriums, and sometimes even the stage space, into smaller theaters.
In most markets, nearly all single-screen theatres (sometimes referred to as a "Uniplex") have gone out of business; the ones remaining are generally used for
arthouse films, e.g. the Crest Theatre
[2] in downtown
Sacramento, California, small scale productions, film festivals or other presentations. Because of the late development of multiplexes, the term "cinema" or "theater" may refer either to the whole complex or a single auditorium, and sometimes "screen" is used to refer to an auditorium.
A popular film may be shown on multiple screens at the same multiplex, which reduces the choice of other films but offers more choice of viewing times or a greater number of seats to accommodate patrons. Two or three screens may be created by dividing up an existing cinema (as Durwood did with his Roxy in 1964), but newly built multiplexes usually have at least six to eight screens, and often as many as twelve, fourteen or even sixteen.
Although definitions vary, a large multiplex with 20 or more screens is usually called a
megaplex however in the United Kingdom this was a brand name for large Virgin Cinema (later UGC). The first megaplex is generally considered to be the
Kinepolis in
Brussels,
Belgium, which opened in 1988 with 25 screens and a
seating capacity of 7,500. The first theatre in the U.S. built from the ground up as a megaplex was the AMC Grand 24 in
Dallas, Texas, which opened in May 1995, while the first megaplex in the U.S. based on an expansion of an existing facility was Studio 28 in
Grand Rapids, Michigan, which reopened in November 1988 with 20 screens and a
seating capacity of 6,000.
Drive-in
A
drive-in movie theatre is basically an outdoor parking area with a screen – sometimes an
inflatable screen – at one end and a projection booth at the other. Moviegoers drive into the parking spaces which are sometimes sloped upwards at the front to give a more direct view of the movie screen. Films are usually viewed through the car windscreen (windshield) although some people prefer to sit on the hood of the car. Sound is either provided through portable
loudspeakers located by each parking space, or is broadcast on an FM radio frequency, to be played through the car's stereo system. Because of their outdoor nature, drive-ins usually only operate seasonally, and after sunset. Drive-in movie theatres are mainly found in the
United States, where they were especially popular in the 1950s and 1960s. Once numbering in the thousands, about 400 remain in the U.S. today. In some cases, multiplex or megaplex theatres were built on the sites of former drive-in theatres.
Other venues

1967 Bedford mobile cinema
Some
outdoor movie theatres are just cleared areas where the audience sits upon chairs or blankets and watch the movie on a temporary screen, or even the wall of a convenient building.
Colleges and universities have often sponsored film screenings in lecture halls. The formats of these screenings include 35 mm, 16 mm, DVD, VHS, and even 70 mm in rare cases.
Some alternative methods of showing films have been popular in the past. In the 1980s the introduction of
VHS cassettes made possible video-salons, small rooms where visitors viewed the film on a large TV. These establishments were especially popular in the
Soviet Union, where official distribution companies were slow to adapt to changing demand, and so movie theatres could not show popular
Hollywood and
Asian films.
In 1967 the British government launched seven custom built
mobile cinema units for use as part of the
Ministry of Technology campaign to raise standards. Using a very futuristic look these 27 seat cinema vehicles were designed to attract attention. They were built on a
Bedford SB3 chassis with a custom Coventry Steel Caravan extruded aluminium body.
Films are also commonly shown on
airliners in flight, using large screens in each cabin or smaller screens for each group of rows or each individual seat; the
airline company sometimes charges a fee for the
headphones needed to hear the films's sound. Films are sometimes also shown on
trains, such as the
Auto Train.
The smallest purpose-built cinema is the Cabiria Cine-Cafe which measures 24 m² (258.3 ft²) and has a
seating capacity of 18. It was built by Renata Carneiro Agostinho da Silva (Brazil) in Brasilia DF, Brazil in 2008. It is mentioned in the
Guinness Book of Records, January, 2010.
The
Bell Museum of Natural History in
Minneapolis,
Minnesota has recently begun summer "bike-ins," inviting only pedestrians or people on bicycles onto the grounds for both live music and movies. In various
Canadian cities, including
Toronto,
Calgary,
Ottawa and
Halifax, al-fresco movies projected on the walls of buildings or temporarily erected screens in parks operate during the Summer and cater to a pedestrian audience.
Programming
Movie theaters may be classified by the type of movies or when they are shown:
- First-run theater: A theater that runs primarily mainstream film fare from the major film companies and distributors, during the initial new release period of each film.
- Second-run or discount theater: A theater that runs films that have already shown in the first-run theaters and presented at a lower ticket price. (These are sometimes known as dollar theaters or "Cheap Seats".) This form of cinema is diminishing in viability owing to the increasingly shortened intervals before the films' home video release, called the video window.
- Repertoire/repertory theater or arthouse: A theater that presents more alternative and art films as well as second-run and classic films (often known as an "Independent Cinema" in the UK).
- An adult movie theater or sex theater specializes in showing pornographic movies. Such movies are rarely shown in other theaters. See also Golden Age of Porn.
- IMAX theaters can show conventional movies, but the major benefits of the IMAX system are only available when showing movies filmed using it. While a few mainstream feature films have been produced in IMAX, IMAX movies are often documentaries featuring spectacular natural scenery, and may be limited to the 45-minute length of a single reel of IMAX film.
Presentation

35 mm movie projector in operation
Usually an admission is for one
feature film. Sometimes two feature films are sold as one admission (
double feature), with a break in between. Separate admission for a
short subject is rare; it is either an extra before a feature film or part of a series of short subjects sold as one admission (this mainly occurs at film festivals). (See also
anthology film.)
Historically, many movie theatres presented a number of shorter items in addition to the feature film. This might include a
newsreel, live-action comedy
short films, documentary short films, musical short films, and/or
cartoon shorts (many classic cartoons series such as the
Looney Tunes and
Mickey Mouse shorts were created for this purpose). Examples of this kind of programming are available on certain DVD releases of two of the most famous films starring
Errol Flynn,
Captain Blood and
The Adventures of Robin Hood as a special feature arrangement designed to recreate that kind of filmgoing experience. Some theatres ran on
continuous showings, where the same items would repeat throughout the day, with patrons arriving and departing at any time rather than having distinct entrance and exit cycles. Newsreels gradually became obsolete by the 1960s with the rise of television news, and most material now shown prior to a feature film is of a commercial or promotional nature.
A typical modern theatre presents
commercial advertising shorts, then
movie trailers, and then the feature film. Advertised start times are usually for the entire program or session, not the feature itself;
[12] thus people who want to avoid commercials and/or trailers would opt to enter later. This is easiest and causes the least inconvenience when it is not crowded, and/or one is not very choosy about where one wants to sit. If one has a ticket for a specific seat (see below) one is formally assured of that, but it is still inconvenient and disturbing to find and claim it during the commercials and trailers, unless it is near an aisle.
Some movie theaters have some kind of
break during the presentation. There may also be a break between the introductory material and the feature. Some countries such as the
Netherlands have a tradition of incorporating an intermission in regular feature presentations, though many theaters have now abandoned that tradition,
[13] while in North America, this is very rare and usually limited to special circumstances involving extremely long movies.
During the
closing credits many people leave, but some stay until the end. Usually the lights are switched on after the credits, sometimes already during them. Some films show additional scenes while the credits are rolling.
Until the multiplex era, prior to showtime, the screen would typically be covered by the traditional curtain which would be drawn for the feature. It is common practice in Australia for the curtain to cover part of the screen during advertising and trailers, then be fully drawn to reveal the full width of the screen for the main feature. Some theaters, lacking a curtain, occupied the screen with slides of some form of
abstract art. Currently, in multiplexes, theater chains often feature a continuous
slideshow between showings featuring a loop of movie trivia, promotional material for the theater chains (such as encouraging patrons to purchase
gift vouchers and group rates, or buy foyer retail offers), or advertising for local and national businesses. Advertisements for
Fandango and other convenient methods of purchasing tickets is often shown. Also prior to showing the film, reminders, in varying forms would be shown concerning theater etiquette (no smoking, no talking, no littering, removing crying babies, etc.) and in recent years, added reminders to silence mobile phones as well as concerning movie piracy.
Some well-equipped theaters have "interlock" projectors which allow two or more projectors and sound units to be run in unison by connecting them electronically or mechanically. This set up can be used to project two prints in sync (for dual-projector 3-D) or to "interlock" one or more sound tracks to a single film. Sound interlocks were used for stereophonic sound systems before the advent of magnetic film prints. Fantasound (developed by
RCA in 1940 for Disney's Fantasia) was an early interlock system. Likewise, early stereophonic films such as
This Is Cinerama and
House of Wax utilized a separate, magnetic oxide-coated film to reproduce up to six or more tracks of stereophonic sound.
Datasat Digital Entertainment, purchaser of
DTS's cinema division in May 2008, uses a time code printed on and read off of the film to synchronize with a CD-ROM in the sound track, allowing multi-channel soundtracks or foreign language tracks. This is not considered a projector interlock, however.
Live broadcasting to movie theaters
Admission prices are often more than twice the regular movie theater admission prices.
Pricing and admission

A typical Malaysian movie ticket.
In order to obtain
admission to a movie theater, the prospective theater-goer must usually purchase a
ticket, which may be for an arbitrary seat ("open" or "free" seating,
first-come, first-served) or for a specific one (
allocated seating).
[15] Movie theaters in North America generally have open seating. Cinemas in Europe can have free seating or numbered seating. Some theatres in Mexico offer numbered seating, in particular, Cinepolis VIP. In the case of numbered seating systems the attendee can often pick seats from a screen; sometimes the attendee cannot see the screen and has to make a choice based on still available seats. In the case of free seats, already seated customers may be forced by staff to move one or more places for the benefit of an arriving couple or group wanting to sit together.
In 2009, the average price for a movie ticket in the United States was $7.50.
[16]The price of a ticket may be discounted during off-peak times e.g. for
matinées, and higher at busy times, typically evenings and/or weekends. In
Australia and
Canada, when this practice is used, it is traditional to offer the lower prices for Tuesday for all showings, one of the slowest days of the week in the movie theatre business, which has led to the nickname "cheap Tuesday."
[17] Sometimes tickets are cheaper on Monday, or on Sunday morning. Almost all movie theaters employ economic
price discrimination: tickets for youth, students, and seniors are typically cheaper. Large theater chains, such as AMC Theaters, also own smaller theaters that show "second runs" of popular films, at reduced ticket prices. Movie theaters in India and other developing countries employ price discrimination in seating arrangement: seats closer to the screen cost less, while the ones farthest from the screen cost more.
In the
United States, many movie theater chains sell discounted passes, which can be exchanged for tickets to regular showings. These passes are traditionally sold in bulk to institutional customers and also to the general public.
[18][19] Some passes provide substantial discounts from the price of regular admission, especially if they carry restrictions. Common restrictions include a waiting period after a movie's release before the pass can be exchanged for a ticket or specific theaters where a pass is ineligible for admission.
Some movie theaters and chains sell monthly passes for unlimited entrance to regular showings. Even if the price is quoted per month the minimum duration may be several months, and when subscribing again after termination a one-time extra fee may be charged. Some examples:
- Pathé Unlimited Card (PUC) for the chain of 16 multi- and megaplex theatres of Pathé in the Netherlands (129 screens), for €18/month.
- Cineville Pass for 13 Amsterdam movie theaters (almost all movie theaters except those of Pathé) for € 17.50 per month.
- Groninger Filmkaart for €20/month for the two movie theaters MustSee Euroborg (10 screens) and Images (3 screens) in Groningen.
- Must See All Card for €18/month for movie theater MustSee Euroborg only.
- Unlimited Card for the chain of movie theaters of Cineworld (formerly UGC) in the UK and Ireland, for £14.99/month, or £17.99 including those in London's West End (plus £1.50 per 3D film viewed) – tickets can only be purchased on the day of the showing.
- Carte Le Pass for the chain of movie theatres of Pathé/Gaumont in 40 French cities (with a total of 790 screens), for 19.80 euro/month.
- UGC Illimité passes for all UGC movie theaters in France, for 18 euro/month, and an entrance fee of 30 euro.
- UGC Unlimited passes for the four UGC movie theaters in Belgium, for 15 euro/month.
- SF Movie Passport pass for all the movies shown in SF Group theaters in Thailand, valid for a month for one person and one showing per movie, at the price of 800 baht or eqv USD 20.
- Membresía Club Cinépolis $125 Pesos(10USD)/month for the regular membership grants access to all the facilities across México for unlimited viewing. 1 Year of forced membership is required. There are also VIP and double memberships.
- Hotlips adult movie theater The Hague, for 55 euro/month.
Note that in Thailand there is the restriction of one viewing per movie, while in the Netherlands one can see any movie as many times as one wants as is the case with the Cineworld UK pass.
The increasing number of 3D films, for which a fee is required, somewhat undermines the concept of unlimited entrance to regular showings, in particular if no 2D version is screened. Also, in one Pathé theater in the Netherlands on one day of the week buying a drink and a snack is compulsory.
Some adult theaters sell a day pass, either as standard ticket, or as an option that costs a little more than a single admission.
Luxury screens
Cinemas in city centers are increasingly offering luxury seating with services like complimentary refills of
soft drinks and
popcorn, a
bar, reclining
leather seats and service bells. The
Vue Cinema chain is a good example of a large-scale offering of such a service, called "Gold Class" and similarly
Britain's largest cinema chain ODEON have gallery areas in some of their bigger cinemas where there is a separate foyer area with a bar and unlimited snacks.
Age restrictions
Admission to a movie may also be restricted by a
motion picture rating system. According to such systems, children or teenagers below a certain age may be forbidden access to theaters showing certain movies, or only admitted when accompanied by a parent or other adult. In some jurisdictions a rating may legally impose this on movie theaters. Furthermore, where movie theaters do not have this legal obligation, they may enforce restrictions on their own.
Accordingly, a movie theater may either not be allowed to program an unrated film, or voluntarily refrain from that. In the US many mainstream movie theaters do not even show movies rated
NC-17 ("No one 17 and under admitted"). Often, instead, an edited R-rated version ("Restricted. Persons under 17 are not admitted unless accompanied by parent or adult guardian.") is shown.
[dubious – discuss]Revenue
Movie studios/
film distributors in the U.S. traditionally drive hard bargains entitling them to as much as 100% of the gross ticket revenue during the first weeks (and then the balance changes in 10% increments at an undetermined time).
[20] See also
box office.
Ticket price uniformity
The relatively strong uniformity of movie ticket prices, particularly in the U.S., is a common economics puzzle, because conventional supply and demand theory would suggest higher prices for more popular movies, and vice versa. Unlike seemingly similar forms of entertainment such as rock concerts, every movie is a unique product. Demand is very difficult to predict ahead of time, and is usually determined from ticket sale statistics after the movie is already out. Uniform pricing is therefore a strategy to cope with unpredictable demand. Historical and cultural factors are sometimes also cited.
[21]Ticket check
In some movie theater complexes, the theaters are arranged such that tickets are checked at the entrance into the entire plaza, rather than before each theater.
At a theater with a sold-out show there is often an additional ticket check, to make sure that everybody with a ticket for that show can find a seat.
The lobby may be before or after the ticket check.
Movie theater culture in USA
Movie theaters are associated with
dating,
popcorn and expensive treats.
Intimacy
Sometimes couples go to a movie theater for the additional reason that it provides the possibility of intimacy, where the dark provides some privacy (with additional privacy in the back-row). This kind of intimacy is considered by some a lesser form of
public display of affection. Compared with being together in a room without other people, it may also be reassuring for one or both of the couple (and for parents) that the intimacy is necessarily limited.
Arm rests pose a hindrance to intimacy for some people. Some theaters have love seats: seats for two without an armrest in the middle. The most modern theaters have movable armrests throughout the theater that when down can hold a food container as well as act as an armrest or partition between the seats and when up allow closer contact between the couple. Some theaters such as the
Parkway in
Oakland, California have sofas for greater comfort.
[22] Foyer area, food and drinks
Movie theaters usually sell various
snack foods and drinks at retail counters or kiosks. Sometimes it can be a self-service where one pays at the counter till, and/or a coin-operated machines. Sometimes the area of sale is more like a self-service shop or kiosk (it is not suitable for consuming the goods), and one pays at the check-out between the shop and the area with the screens. Foods usually served at movie theatres include
popcorn,
soft drinks,
nachos,
hot dogs,
ice creams and a wide range of
confectionery. At most theatres, people are allowed to select their own sweets (known as "
pick and mix".)
The facilities for buying snacks and drinks often represent the theater's primary source of profit since most of the ticket revenue goes to the film distributor (and onward to the movie studio)
[citation needed]. Some movie theaters forbid eating and drinking inside the viewing room (restricting such activities to the foyer), while others encourage it by fitting
cup holders on the arm rests (on the front side of the arm rests of one's own chair, or the back side of the arm rests in front) and selling large portions of
popcorn and soft drinks; also in that case bringing one's own food and drinks may be forbidden. Retail is currently a huge area of expansion with many companies in the U.S. offering a wider range of snacks, including
hot dogsand
nachos.
Many theaters have embraced the "brew and view" concept, serving alcoholic beverages, in addition to snacks and popcorn. Some movie theaters such as the
Alamo Drafthouse offer full restaurant service at one's seat, though this is not as widespread.
McMenamins is a chain of
restaurant/
brewpub establishments in the U.S. states of
Oregon and
Washington, many of which have full movie theaters.
Some movie theaters feature a wider selection than simply snacks and popcorn. These "dine-in" theaters allow patrons to purchase "meals" (ranging from pizza slices to hamburgers and more) that can be consumed while watching the movie.
The health benefits of this cinema food are generally low, and have been debated for years. Owner of
Sony Pictures, Michael Lynton, has been one of the chief arguers over this, and has wanted cinemas worldwide to stop providing this junk food and instead provide healthier alternatives, like crudites, smoothies, nuts, granola bars and additive-free air-popped popcorn.
 17.06
17.06
 gamal_cink
gamal_cink



 Beranjak dari 16 tahun kesuksesan Waterbom Bali, pada tahun 2007 Waterbom Jakarta resmi dibuka. Komitmen kami tidak pernah berubah untuk selalu mejadi yang terbaik dalam pelayanan, fasilitas, desain dan estetika. Dengan tema Urban Cool, desain lansekap indahnya menawarkan atomosfir yang santai dengan wahana airnya yang mengasyikkan sekaligus menegangkan. Nama Waterbom kini telah diakui sebagai pemimpin dalam pelayanan, hiburan dan standarisasi yang tinggi.
Beranjak dari 16 tahun kesuksesan Waterbom Bali, pada tahun 2007 Waterbom Jakarta resmi dibuka. Komitmen kami tidak pernah berubah untuk selalu mejadi yang terbaik dalam pelayanan, fasilitas, desain dan estetika. Dengan tema Urban Cool, desain lansekap indahnya menawarkan atomosfir yang santai dengan wahana airnya yang mengasyikkan sekaligus menegangkan. Nama Waterbom kini telah diakui sebagai pemimpin dalam pelayanan, hiburan dan standarisasi yang tinggi. Waterbom Jakarta menawarkan proses penjernihan air tingkat lanjut yang unik dan tanpa kaporit. Kualitas air kami sangat ramah lingkungan dan kesehatan manusia terutama kulit, mata dan rambut. Demi keselamatan pengunjung, seluruh lifeguard kami melewati ujian untuk mendapatkan sertifikat dan lolos uji international Safety Guard Standard. Dokter jaga yang selalu siap selama jam operasional, sistem keamanan terpadu di seluruh areal taman, parkir yang nyaman dan akses yang mudah dari jalan tol.
Waterbom Jakarta menawarkan proses penjernihan air tingkat lanjut yang unik dan tanpa kaporit. Kualitas air kami sangat ramah lingkungan dan kesehatan manusia terutama kulit, mata dan rambut. Demi keselamatan pengunjung, seluruh lifeguard kami melewati ujian untuk mendapatkan sertifikat dan lolos uji international Safety Guard Standard. Dokter jaga yang selalu siap selama jam operasional, sistem keamanan terpadu di seluruh areal taman, parkir yang nyaman dan akses yang mudah dari jalan tol.























